What is food waste management?
The FAO defines food waste as. “…food appropriate for human consumption being discarded, whether it’s kept beyond its expiry date or left to spoil”.
Food waste management encompasses the stages of prevention, recovery, recycling, and disposal of food waste.
This includes:
- Food waste tracking and prevention
- Food banks
- Using food as animal feed
- Creating renewable energy through anaerobic digestion
- Composting
- Landfills
Stages of food waste management
The most important stage of food waste management is reducing the waste of edible food. Traditionally, tracking food waste hasn’t been a priority for commercial kitchens.
The majority simply don’t know how much food they’re throwing away, and in turn, how much money is wasted. Even if they do, most kitchens are limited to rudimentary food waste tracking spreadsheets, which take up valuable staff time and result in inaccurate data. This causes most businesses to vastly underestimate their food waste.
For hospitality businesses, it’s critical to have a robust food waste tracking process in place to reduce their carbon footprint and save money. Thankfully, technology has enabled a new era for food waste management, often in the form of software enabled with hardware to fit the rugged kitchen environment.
Management of Waste
With technology replacing the vast majority of the data collection process, managing waste is now a straightforward five-step process.
- Food is thrown into the designated food waste bin.
- The weight of the waste is logged from the scale under the bin, and the food type is captured on camera.
- This process is repeated over the course of the day and has the capability to include cooking errors, overproduction, trimmings, and plate waste.
- The data is sent to the cloud, where it is aggregated, including the financial and environmental costs of the wasted food, time of day, and areas in production of high waste. Chefs can view the waste the next day.
- With this insight available in an actionable format, the chefs can now make operational decisions in the kitchen to reduce waste.

Challenges in food waste management
Why is food waste a global issue?
Food waste impacts every country on earth and adversely impacts climate change.
Greenhouse gases are produced at every stage of the food chain, including the methane emitted when organic matter is dumped in the rubbish tip. In fact, according to FAO, if food waste were a counter,y it would be the 3rd largest emitter of greenhouse gases (after China and the USA).
The way land is utilised in agriculture contributes to food waste on a massive scale. Arable land used to grow uneaten cereals contributes to 4–15% of food wastage in each region. Shockingly, an area larger than China is used to grow food that is never eaten.
Food waste is also an ethical issue when you take into account the 800 million people who don’t have access to food in the same way as developed countries, and the many people in developed countries living in food poverty.
To solve global hunger, we need to dramatically reduce the volume of food loss within our system.
Hotel Food Waste Management
Reducing and managing food waste to operate more sustainable hotel kitchens has been a hot topic in the industry this year. MICE (meetings, incentives, conferences, exhibitions) are a big source of food waste, and customers are increasingly looking for hotels that demonstrate ESG credentials. There are several excellent examples of hotels that are getting it right.
The team at Marriott Hotel’s Grosvenor House Dubai is constantly looking for new ways to become more sustainable and improve their operations. Creeks helped Culinary Director Marco Torrass understand the volume and different varieties of food that were thrown away each service.
With this information, they were able to look into various areas to either reduce the amount of food production, increase the use of various food items, or re-use the food for their staff canteen.
As a result, in the first year:
- Food waste was reduced by 72%
- 50,000 meals were saved in a year
- Approximately 300,000 AED ($81,000) was saved
What are the main causes of food waste?
Food is wasted for a variety of reasons, starting with the initial stages of the supply chain. Processing issues, overproduction, and unstable markets cause food waste before it even arrives at a commercial kitchen.
Once it does arrive, kitchen management plays its part in food waste by overbuying produce, poor planning, and overproduction of food. Oakdene Hollins found that 66% of food waste in commercial kitchens is pre-consumer waste, and 34% is post-consumer waste.
At the final stage, aerobic fermentation facilities, which turn waste into environmentally friendly organic fertilizer, are an option. However, it’s better to reduce surplus food at the outset rather than turn it into energy.
Catering Food Waste Management
For companies in the catering and services sector, optimising food waste costs is essential.
Amid the complexities the pandemic caused, contract catering emerged as a more agile and resilient industry. Consumer preferences have pivoted and now include a growing focus on sustainability.
The World Economic Forum and Ipsos found that 86% of people want to see a significant change towards a more equitable and sustainable world after the pandemic.
Larger catering companies, like Compass Group or ISS Facility Services, operate thousands of kitchens across the globe and are taking the initiative to reduce food waste and enhance customer experience, all while saving money.
Food waste management offers huge potential in mitigating greenhouse gas impact and has the potential to save catering operations between 3% and 8% on food costs.
This equates to millions of tonnes of CO2e annually, and billions of dollars that could be saved.
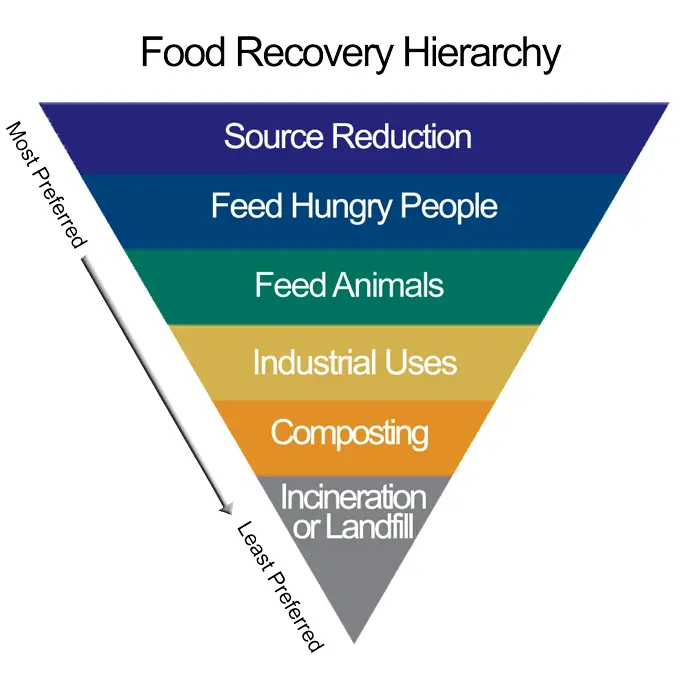
How management can reduce food waste
When it comes to reducing food waste in kitchens, management play a key role in establishing a culture of waste prevention.
There are six ways businesses can deal with food waste, which are prioritised by the food recovery hierarchy.
- Source reduction. Minimising the amount of food you’re buying or reducing the number of items on a menu.
- Feed hungry people. Helping your community by donating food to food banks, soup kitchens, or shelters.
- Feed animals. Helping to sustain the local farming industries to help turn scraps from your kitchen into animal food.
- Industrial uses. Working with local councils to repurpose kitchen items. Wasted oils can be rendered and turned into a sustainable fuel source, while food scraps can be anaerobically digested and help create energy.
- Composting. Repurposing food waste as compost with local crop producers in your community.
- Incineration or landfill. This is not sustainable or environmentally friendly. Measures should be taken to avoid this action for all food waste.
What’s the best way to manage food waste in restaurants?
There are several things you can do to avoid food waste. Conducting a food waste audit is one of them.
It’s important to get an understanding of the stage of service or point during the day which is particularly high in waste produce, so you can put measures in place to prevent this.
The complexity of gathering this information depends on the type of operation you work in, but see if you can estimate the answers to the following questions during your next service:
- What are the top three food produce items being thrown away throughout the day?
- What’s the weight and value of the most valuable item?
- If you wasted produce to the same level every day, what would that figure look like over a year of service?
- If you can answer these questions, you’ll be surprised by the value of the products being thrown away. Making decisions informed by this data is key to avoiding food wastage in your kitchen.
- Carrying out food audits manually, on an ongoing basis, is a time-consuming, inaccurate, and laborious process.
This is where technology can support this manual data collection and analysis, and ensure kitchen teams can get back to cooking while having the insight needed to reduce food waste and kitchen costs.
Managing food waste is beginning to have legal implications for businesses, too. In France, it’s now illegal for supermarkets to throw away food.
Fines can be up to €75,000, or two years imprisonment.
Tools for Food Waste Management
With increasing awareness of sustainability and cost efficiency, businesses and individuals are adopting various tools to track, reduce, and manage food waste effectively. These solutions help minimize environmental impact, cut costs, and comply with waste regulations.
On-Site Food Waste Composting Machines
For businesses generating large amounts of organic waste, composting machines offer an efficient way to process scraps sustainably. Creeks Food Waste Composting Machine – Rapidly decomposes food waste into compost, reducing landfill contributions and odor.
