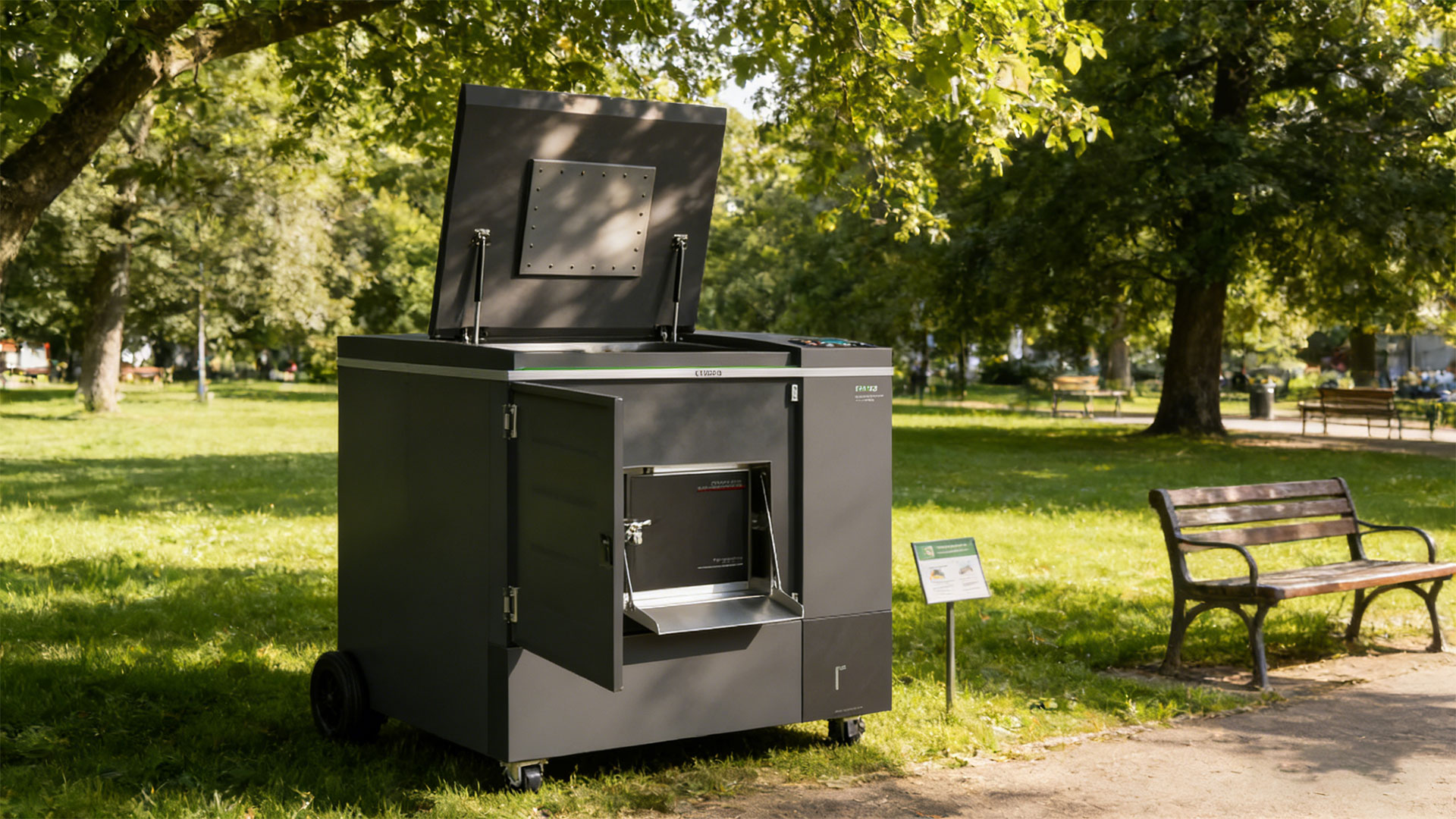
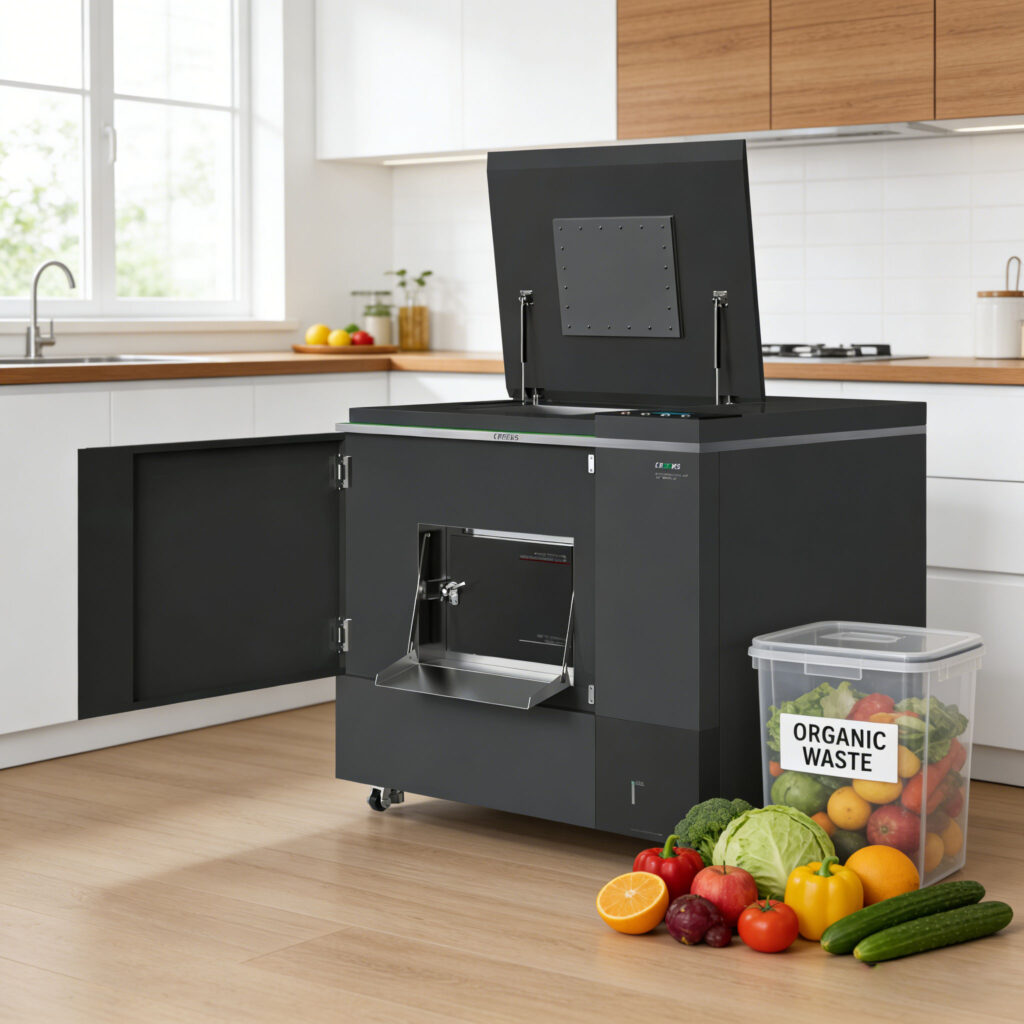
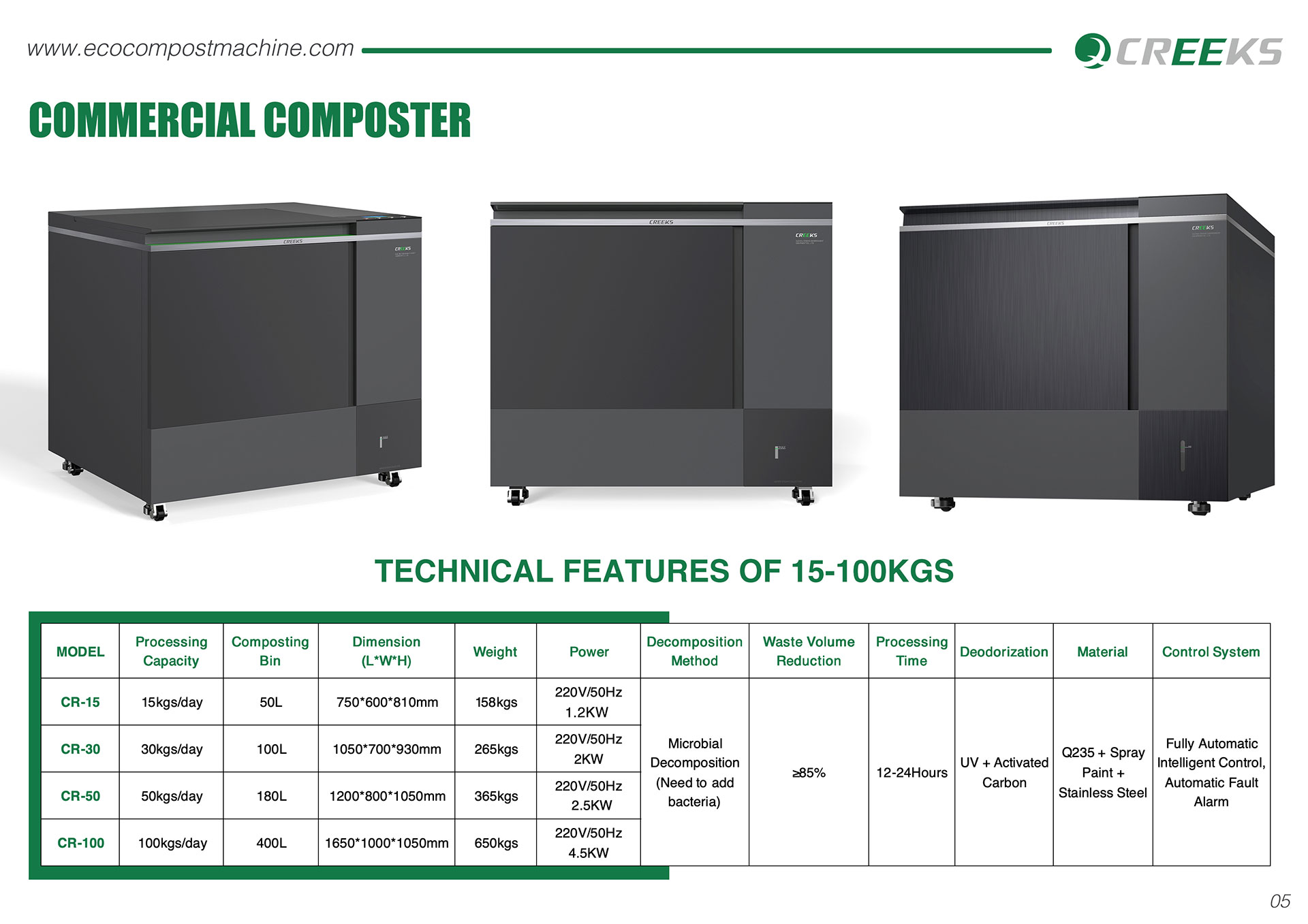
What is a Food Waste Machine?
A Food Waste Machine is a device designed to process organic food waste (like kitchen scraps, leftovers, and spoiled food) on-site, reducing its volume, weight, and environmental impact. It accelerates the natural decomposition process through mechanical and biological means, offering an alternative to landfilling.
Core Objectives
- Volume/Weight Reduction: To reduce waste by up to 90% (by volume) and 80-85% (by weight).
- On-Site Management: To handle waste where it’s generated, cutting transportation costs and emissions.
- Environmental Sustainability: To divert waste from landfills, where it would produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Resource Recovery: To transform waste into a useful byproduct – compost.
How a Food Waste Machine Works?
- Collection & Loading: Food waste is collected in kitchen bins and loaded into the machine’s chamber.
- Shredding: Internal blades shred the waste into small, uniform particles, increasing the surface area for microbial action. (Optional Function)
- Decomposition Phase: Heated, oxygen-rich air is circulated. Microbes (thermophilic bacteria) rapidly consume the waste, raising the temperature high enough to kill pathogens.
- Moisture & Aeration Control: The system carefully manages moisture and air to optimize the process.
- Curing & Output: After the active cycle, the material may cure. The final output (dry mulch, compost, or liquid) is collected for use or disposal.
Key Benefits & Advantages of Food Waste Machine
- Reduces Landfill Impact: Diverts organic waste, reducing methane emissions and landfill leachate.
- Lowers Costs: Cuts waste hauling and tipping fees.
- Saves Space: Drastically reduces the volume of waste stored on-site.
- Hygiene & Odor Control: Enclosed systems control pests, odors, and bacteria.
- Creates Value: Produces useful compost for landscaping or agriculture.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Demonstrates a commitment to sustainability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet local waste diversion and organic waste ban regulations.
Common Applications & Users
- Commercial: Hotels, restaurants, supermarkets, shopping malls.
- Institutional: Hospitals, schools, universities, prisons, corporate cafeterias.
- Industrial: Food manufacturing and processing plants.
- Public/Municipal: Airports, cruise ships, stadiums, municipal waste centers.
- Residential: Large apartment complexes and gated communities.
At Creeks, we believe the challenge of a growing population—and the corresponding rise in waste—calls for shared responsibility and immediate action. While waste reduction remains essential, we also recognize that some by-products are inevitable. That’s why we’re committed to transforming what remains into valuable resources.
To help you turn waste into worth, we provide a range of equipment tailored to different volumes and needs—because sustainable solutions should fit seamlessly into your operations.